Introduction
Salesforce Hyperforce is a significant innovation in the realm of cloud computing, specifically tailored for Salesforce customers. As businesses evolve and data requirements expand, the need for scalable, secure, and compliant cloud infrastructure becomes critical. Hyperforce addresses these needs by reimagining Salesforce’s architecture, making it more robust, flexible, and aligned with the diverse regulatory requirements across the globe.

Why Salesforce Hyperforce Was Created
Salesforce created Hyperforce to address several emerging challenges and opportunities in the cloud computing landscape:
- Scalability: Traditional Salesforce architecture, while robust, had limitations in handling massive and rapidly growing datasets. Hyperforce offers enhanced scalability, allowing businesses to expand without worrying about infrastructure constraints.
- Global Compliance: With data regulations becoming increasingly stringent worldwide, Salesforce needed a solution that could offer compliance with various local regulations. Hyperforce provides the flexibility to store data in specific geographic locations, ensuring compliance with regional laws like GDPR in Europe and CCPA in California.
- Performance and Latency: By leveraging the power of public cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, Hyperforce significantly reduces latency and improves performance, ensuring faster response times and a better user experience.
- Security: Hyperforce is designed with a security-first approach, incorporating advanced security measures and providing customers with more control over their data.
Architecture of Salesforce Hyperforce
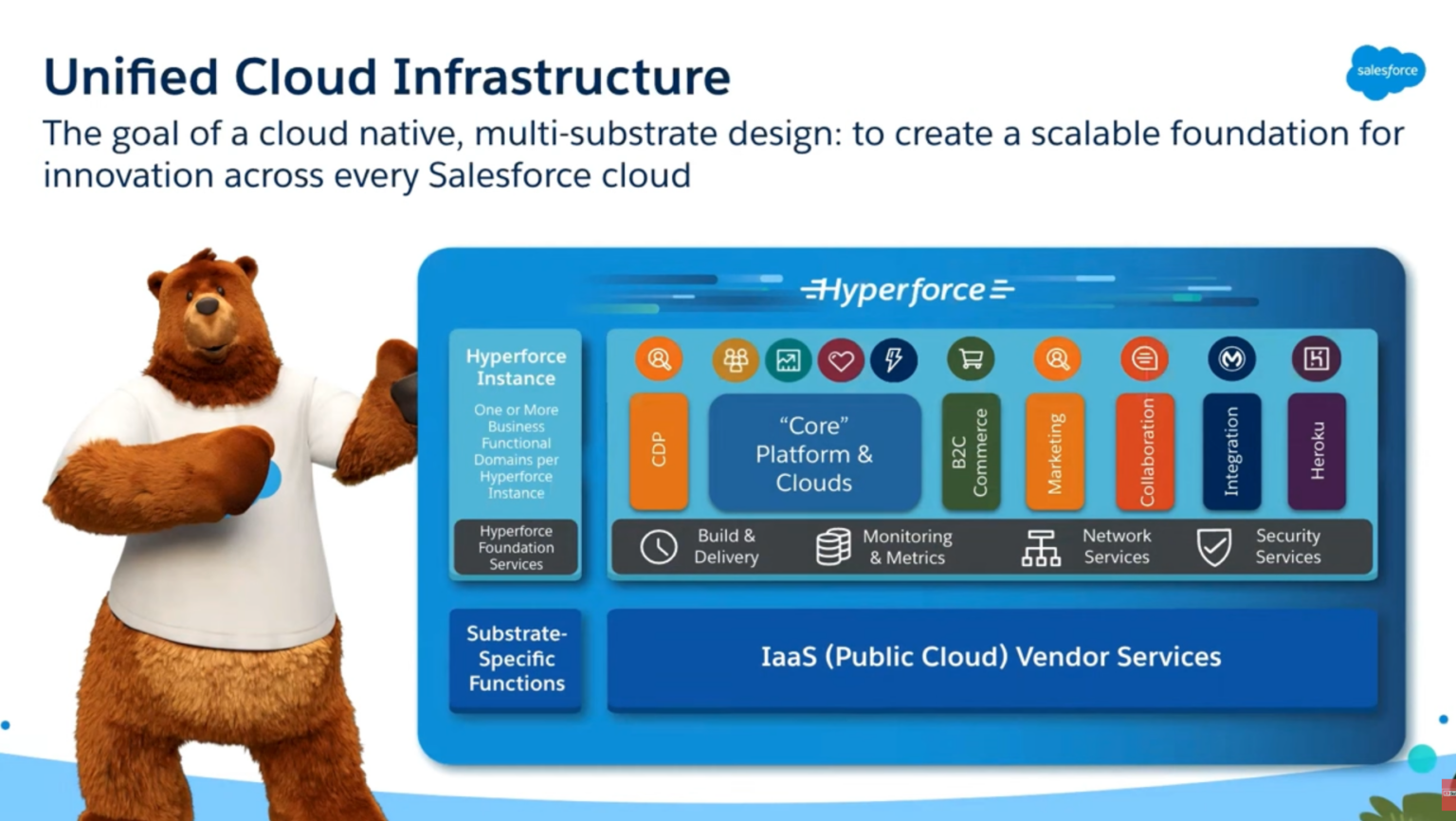
The architecture of Salesforce Hyperforce is a radical departure from the traditional Salesforce architecture. It integrates with major public cloud providers, offering several benefits:
- Public Cloud Integration: Hyperforce utilizes the infrastructure of leading public cloud providers. This means Salesforce instances can now be deployed in the data centers of AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud, depending on the customer’s preference and regional availability.
- Containerization: Hyperforce uses containerization technology to package Salesforce applications and dependencies. Containers provide an isolated environment, ensuring consistency across different deployment environments and enhancing security and scalability.
- Microservices: The architecture leverages microservices, breaking down the monolithic Salesforce application into smaller, manageable services. This modular approach allows for independent scaling, development, and deployment of different components, enhancing agility and resilience.
- Data Residency Control: Hyperforce allows customers to choose where their data is stored, providing more control over data residency. This feature is crucial for complying with regional data protection regulations.
- Encryption and Security: Data encryption is a fundamental aspect of Hyperforce. It ensures data is encrypted both at rest and in transit, using advanced encryption standards. Additionally, Hyperforce incorporates robust identity and access management (IAM) controls, ensuring that only authorized users can access sensitive data.
Problems Solved by Salesforce Hyperforce
Hyperforce addresses several critical issues faced by businesses using Salesforce:
- Compliance with Local Regulations: By offering data residency control, Hyperforce ensures that businesses can comply with local data protection laws, reducing legal and compliance risks.
- Improved Performance: Leveraging the infrastructure of leading cloud providers, Hyperforce offers improved performance and reduced latency, enhancing the overall user experience.
- Scalability: Hyperforce can scale resources dynamically based on demand, ensuring that businesses can handle large volumes of data and transactions without performance degradation.
- Security: Enhanced security features in Hyperforce provide robust protection against data breaches and unauthorized access, ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of customer data.
Best Practices for Migrating to Hyperforce
Migrating to Salesforce Hyperforce requires careful planning and execution. Here are some best practices to ensure a smooth transition:
- Assessment and Planning: Begin with a comprehensive assessment of your current Salesforce environment. Identify all customizations, integrations, and data volumes. Develop a detailed migration plan that includes timelines, resource allocation, and risk mitigation strategies.
- Data Governance: Establish strong data governance practices. Ensure data quality and integrity before migration. Define data residency requirements and ensure compliance with regional regulations.
- Testing and Validation: Conduct thorough testing at every stage of the migration. Use sandbox environments to test data migration, application functionality, and performance. Validate that all customizations and integrations work seamlessly in the new environment.
- Security Considerations: Review and enhance security measures. Implement advanced encryption, IAM controls, and ensure that all security policies are adhered to in the Hyperforce environment.
- Training and Change Management: Provide training for your team to familiarize them with the new environment. Develop a change management strategy to ensure a smooth transition and minimize disruptions to business operations.
- Continuous Monitoring and Optimization: After migration, continuously monitor the performance and security of your Salesforce environment. Optimize resources and configurations based on usage patterns and business requirements.
Gotchas in Salesforce Hyperforce Migration
While Hyperforce offers numerous benefits, there are some potential challenges and “gotchas” to be aware of during the migration process:
- Compatibility Issues: Some legacy customizations and integrations may not be fully compatible with Hyperforce. It’s crucial to identify and address these issues during the planning and testing phases.
- Data Transfer Complexity: Migrating large volumes of data can be complex and time-consuming. Ensure you have the necessary tools and resources to handle data transfer efficiently.
- Performance Tuning: Initial performance tuning may be required to optimize the new environment. Be prepared to fine-tune configurations to achieve the desired performance levels.
- Regulatory Compliance: While Hyperforce offers enhanced compliance capabilities, it’s essential to thoroughly understand and implement the specific regulatory requirements relevant to your industry and region.
- Cost Management: Transitioning to Hyperforce may involve additional costs, including those for data transfer, new infrastructure, and potential reengineering of applications. Plan and budget accordingly to avoid unexpected expenses.
Salesforce Hyperforce represents a significant leap forward in cloud architecture, addressing the evolving needs of businesses for scalability, compliance, performance, and security. By leveraging the power of public cloud providers and modern technologies like containerization and microservices, Hyperforce offers a robust and flexible platform for Salesforce customers.
Careful planning, thorough testing, and adherence to best practices are essential for a successful migration to Hyperforce. While there may be challenges along the way, the benefits of improved performance, enhanced security, and compliance with local regulations make Hyperforce a compelling choice for businesses looking to future-proof their Salesforce environment.
Also see: Introducing Hyperforce – General Information & FAQ (salesforce.com)
